The text, images, audio, video, links, and other web content that you see on the webpage, from simple blogs to the massive e-commerce site, are possible with HTML. HTML is the essential technology and acts as the foundation of the Web.
This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide on HTML, covering topics like what is HTML, what HTML tags and elements are, what you can do with html, and why it is worth learning HTML in 2026, where AI is booming.
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, used to create, structure, and display different types of content in a web browser. In simple words, HTML is known as the skeleton of a webpage that uses various tags and elements to show documents like text, images, headings, videos, and links on the website.
HTML is not a programming language, but a markup language, which means the content is connected with each other using numerous predefined tags such as <p>, <img>, <h1>, and </br>. The HTML tags are opening, closing, and some are self-closing tags. Let’s break down the meaning of HTML:
- HYPER: It means the content on the web refers to or links to somewhere. Used to connect related items.
- TEXT: Data or information on the web.
- MARKUP: Predefined/ Marked on somewhere on the web. For example:
a) Images are marked using the <img> tag.
b) Paragraph is marked using the <p> tag.
c) Form is marked using the <form> tag - LANGUAGE: A language that a computer can understand for interpretation
The basic structure of HTML is used on almost every website you find on the web. This structure consists of predefined tags, elements, and attributes to tell the browser how the content should be shown on the web.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<title> First Webpage of WPVOID</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>WPVOID Heading</h1>
<p>First paragraph of WPvoid site.</p>
</body>
</html>
The basic structure of HTML is used on almost every website you find on the web. This structure consists of predefined tags, elements, and attributes to tell the browser how the content should be shown on the web.
The html basics structure includes the following key components:
1) <! DOCTYPE html>
The DOCTYPE tells the browser the version of HTML, and in this case, the version is HTML5. This is the very first tag of any website
2) <html lang="en-US">
It refers to the language of the content in the HTML. Here, “en-US” defines the language as the United States.
3) <html> </html>
The enclosed HTML tags are the root elements of an HTML page. All the essential components must be contained within this tag, including head, title, and body. It also includes the lang attributes to declare the language of the page, like <html lang= “en-US”>.
4) <head></head>
The head tag contains meta information about the HTML document, such as the title of the site, CSS styles, scripts, character set, and meta information
5) <meta charset="UTF-8">
The meta charset determines the character encoding for the document, making sure the browsers correctly display the text.
6) <title>Page Title</title>
-The title tag defines what text/string should appear in the window title bar or browser tab when the page loads. The text you see on the browser tab is taken from the title tag.
7) <body></body>
The body tag contains all the visible content that you see on the webpage. This includes the images, text, videos, links, and all the semantic and structural elements that you see on the webpage. The html, title, and head tags are not included in this tag.
8) <h1>...</h1>
The h1 tag comes under the body tag, which represents the main heading of the webpage, and can go up to <h7>.
9) <p>...</p>
The p tag is placed inside the body tag and used to display blocks of text or paragraphs on the webpage.
Every HTML Element begins with Tags and uses Attributes to structure and style the web content efficiently. Let’s see the meaning of tags, elements, and attributes.
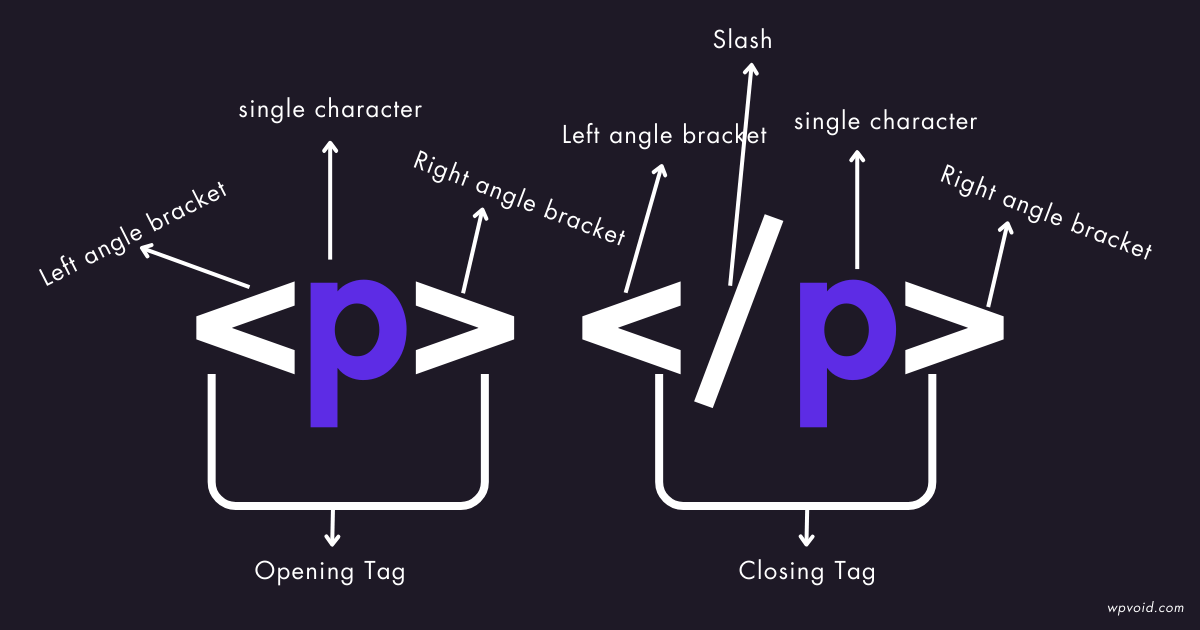
HTML Tags can be defined as the predefined markup for the web or a set of characters enclosed in angle brackets(<>). Tags usually come in pairs, i.e, opening tag and closing tag, while some tags are self-closing tags.
i) Opening Tag: <tagname> ( e.g., <p>)
ii) Closing Tag: </tagname> (e.g., </p>)
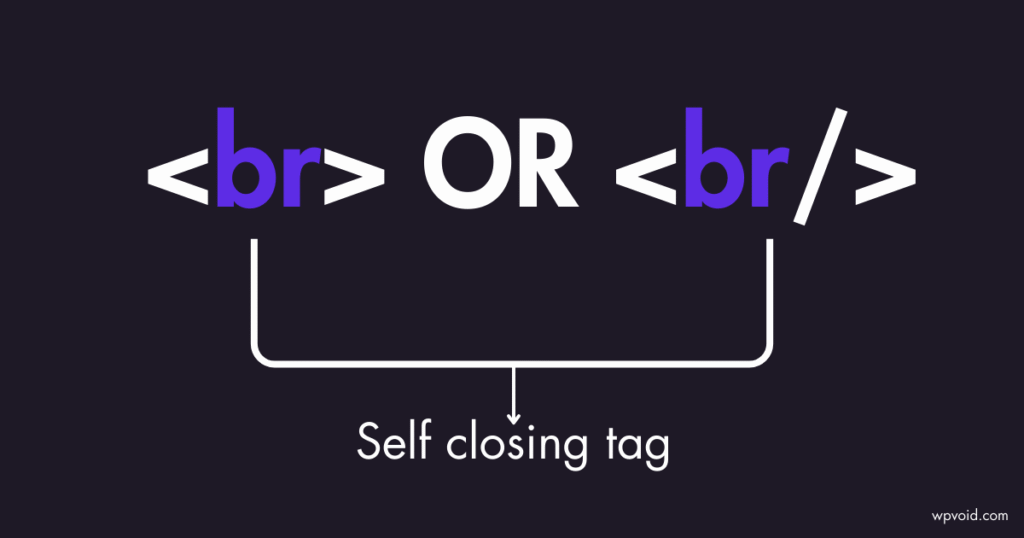
iii) Self-Closing Tag: </tagname> (e.g., </br>)
Some examples of tags are:
i) <p> </p> = To write a block of text, we can use the P tag.
ii) <b> </b> = The B tag is used to bold the content.
iii) <a> </a> = For URL or link, the a tag can be used.
iv) <h1> </h1> = The H1 tag is considered the top heading in a web.
v) </br>= The Br tag is used to break the line in a web document.
vi) <img>= The img self-closing tag is used to display an image on the web.
In Summary, it can be said that the ‘p’ tag is used for paragraphs, the ‘b’ tag is used to bold the content/text, the ' a 'tag is used to link the text/content, the ‘h1’ tag is used as a top heading, 'br' tag is used to break the line, and the 'img' tag is used to show the image.
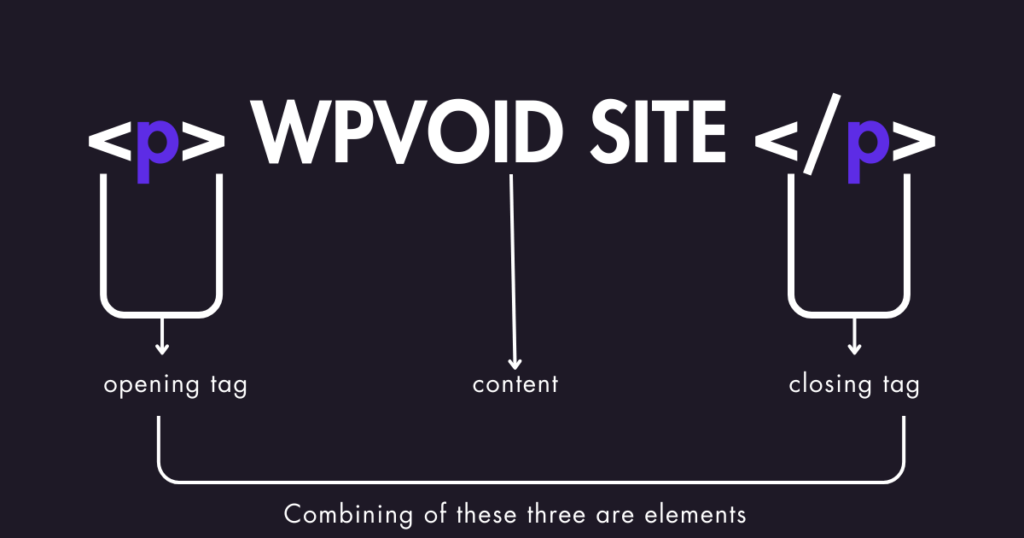
An HTML Element is a complete unit that consists of an opening tag, attributes, content, and a closing tag. It represents the structure and meaning of the content on the web.
The typical example of the element:
Opening Tag + Attribute + Content + Closing Tag = Element
Example: < a href= “wpvoid.com” > Homepage </a>
Here, the “<a>” is an opening tag, “href= “wpvoid.com” refers to an attribute, “Homepage” is content, and </a> is a closing tag of the element.
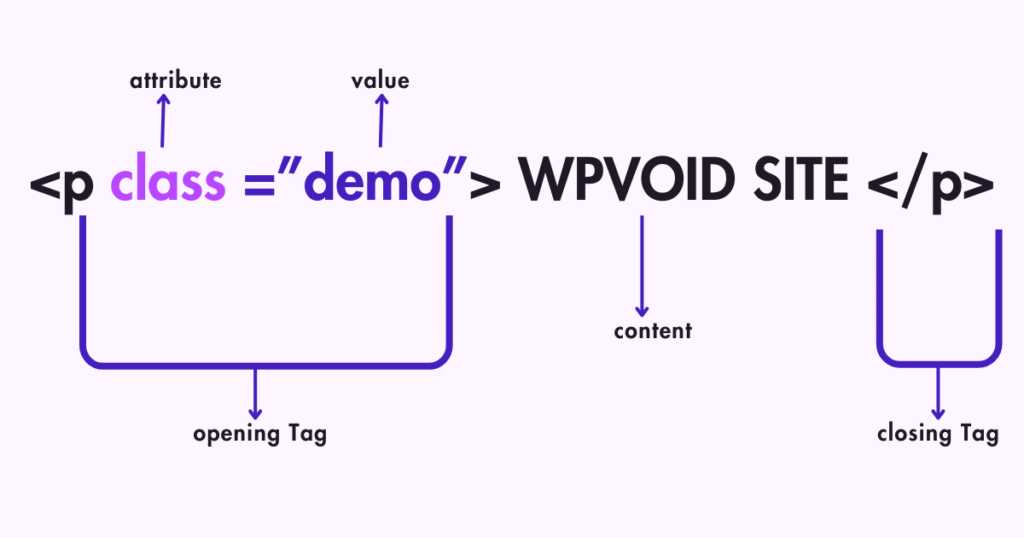
An HTML Attribute gives additional information about the elements and should be placed within the opening tag. They always come in name/value pairs like name=” values ”. Here are some of the HTML attributes with their purpose and examples.
|
Attribute |
Purpose |
Element Example |
|---|---|---|
|
src |
Represents the path of an image or other media |
<img src= "wpvoid_logo.png"> |
|
href |
Specifies the URL that points to a specific link |
< a href= “wpvoid.com” > Homepage |
|
class |
Used to assign a CSS class to an element for styling. |
< p class= "warning-text" >Caution </p> |
|
alt |
Specifies alternative text for an image |
<img src="wp_home.png" alt="Home logo"> |
The first version of HTML was invented in 1991 and released in 1993 for the purpose of sharing or publishing documents more efficiently by Sir Timothy John Berners-Lee, popularly known as Tim Berners-Lee, a physicist at the CERN research institute in Switzerland.
Berners-Lee is also known for the invention of the World Wide Web (WWW) in 1989, while working at CERN, and other Web core systems like Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Uniform Resource Locator (URL).
The latest version of Hyper Text Markup Language(HTML), i.e., HTML 5, was initially released in 2014 and developed by Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group ( WHATWG ) and World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), while focusing on syntactic features such as <video>, <main>, <footer>, <nav>, and so on.
Initially, the early version of HTML lacked features such as Video, Audio, Canvas, and Style, which were introduced in the later version, i.e., HTML5. Here is the table describing the availability of HTML features according to their version.
|
Type of Content |
HTML 1.2 |
HTML 4.01 |
HTML 5 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Image |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Paragraph |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Heading |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Anchor |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
List |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Address |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Style |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Table |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Script |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Audio |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
Video |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
Canvas |
No |
No |
Yes |

Image: Tim Berners Lee, inventor of HTML, sitting on his computer, working at CERN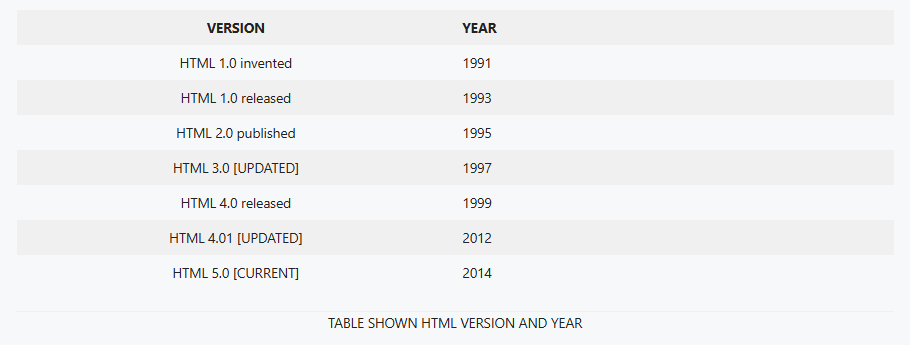
XHTML, XML, and DHTML are historical markup languages like HTML. Before the dominance of HTML5, web developers explored different alternatives like XHTML, XML, and DHTML for creating dynamic and structured web content to make the documents more accessible, easy to display, and store data among the elements.
XHTML stands for Extensible Hyper Text Markup Language, which was developed to make HTML stricter by applying XML rules that required all tags to be in lowercase and should be properly closed. The main motive of XHTML is to make the code cleaner and more predictable as it uses lowercase tags and proper nesting.
Some features of XHTML are:
Here are some of the key features and requirements of XHTML:
a) The <!DOCTYPE> declaration on the first line and the root element, such as <html>, < head>, <title>, and <body> tags, were all mandatory in XHTML.
b) XHTML was case sensitive, meaning all the elements and attributes should be written in lowercase.
c) Every element had to have a closing tag, and should be properly nested.
d) The entire document content should be contained within a single root element, i.e., the <html> tag.
To convert your HTML code into XHTML, you can simply follow these steps:
Step 1-> Add Doctype: Place the <!DOCTYPE> on the first line of every XHTML page.
Step 2-> Add Namespace: Make sure to include attributes like “xmlns” within the <html> tag.
Step 3-> Lowercase Tags: Write all the element and attribute names in lowercase.
Step 4-> Quote Attributes: All the attribute values should be in quotation marks ( “ ” ).
Step 5-> Closing Tag: All elements should be explicitly closed, including the void elements such as <br/>.
Step 6-> Nest Properly: Ensure all the elements in the XHTML code are nested properly. (e.g., <b><i> Nested Text </i> </b>).
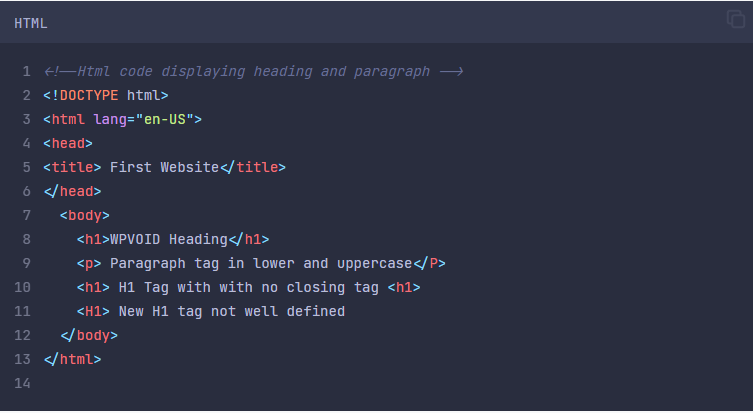
Here, the code is written in HTML5 with various errors, such as Sentence Case in the P tag, and the H1 tag is undefined. It will display the output correctly, ignoring all the errors. Therefore, HTML5 is not stricter than XHTML.

Here, HTML doesn’t show any error while executing this file. Now, let's see the same program in XHTML.
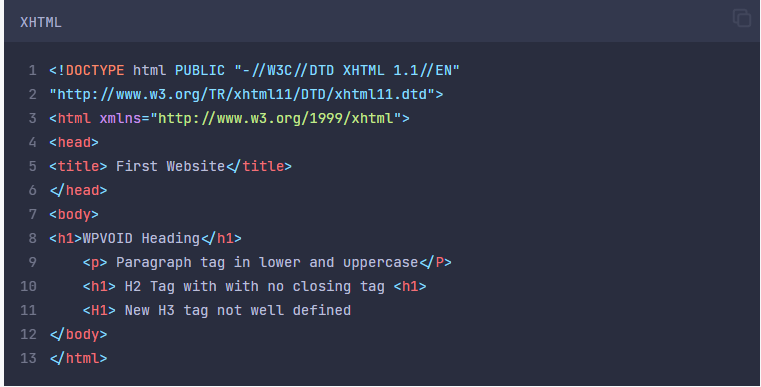
Image:Code in XHTML with incorrect syntax or tag 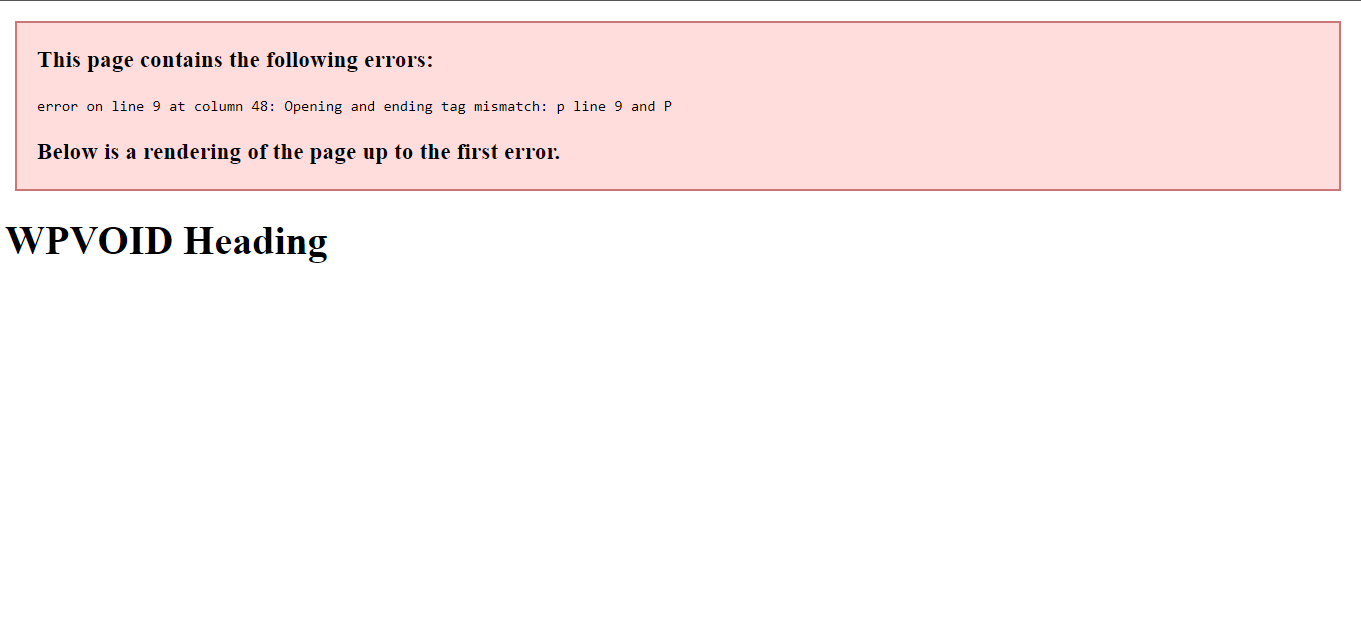
Here, XHTML throws an error on a tag that was not properly managed. So, we can conclude that XHTML is stricter compared to HTML, and the rules and protocol should be followed in order to execute it properly.
To run an XHTML file, you can simply follow these simple steps:
Step 1=> Choose Editor: Select a code editor like Sublime Text, WebStorm, Visual Studio Code, or a Note pad to write and edit the code.
Step 2=> Write Code: Create your document or code while strictly following all the XHTML rules.
Step 3=> Save File: Use “ .xhtml ” [ dot xhtml ] file extension to save the code.
Step 4=> Execute in Browser: Now, open the saved file to run in the browser. If all the code is correct and nested properly, it will execute; otherwise, you might face an error to debug.
DHTML stands for Dynamic Hyper Text Markup Language. It was not a language but a technology that combines HTML, CSS, and JavaScript with the DOM to create client-side interactive and animated effects on websites while supporting server-side script or database connectivity.
The code below of DHTML contains HTML, CSS, and JS in the same file.
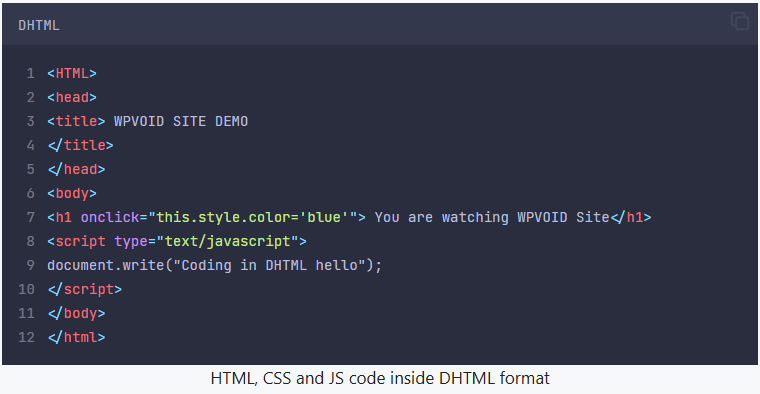
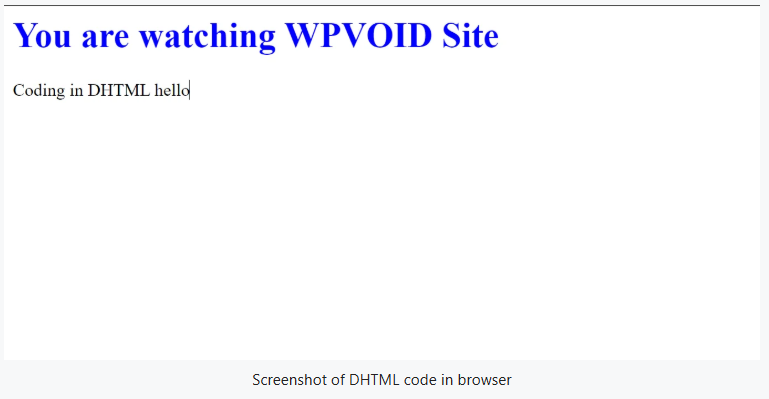
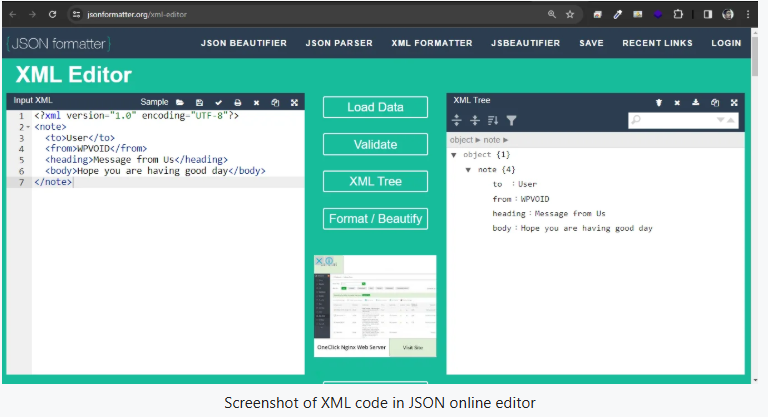
XML is the short form of Extensible Markup Language. It was never meant for web display but to store and transport data between systems using user-defined custom tags. Moreover, XML has one root element, and the sub-root elements must be enclosed inside the root element.
Features of XML elements:
a) All the elements are case sensitive, which means <Book> is considered a completely different element from <book>.
b) The elements of an XML should begin with a letter (A-Z or a-z) or an underscore (_).
c) Elements of an XML cannot use reserved keywords like XML.
d) The use of white space is prohibited in XML element names, and some characters are forbidden, like !, @, $, etc.

To create and execute an HTML file, follow these simple steps:
Step 1=> Choose Code Editor: Select a html editor like Sublime Text, Atom, Visual Studio Code, or Notepad to write and edit the HTML code.
Step 2=> Write Code: Create your document or html code, beginning with the necessary declaration and the html basics structure.
Step 3=> Save File: Use “ .html ” or “ .htm ” [ dot xhtml or dot htm ] file extension to save the code.
Step 4=> Execute in Browser: Now, open the saved file for html preview in the browser. The browser will interpret the code and display the structured content as a functional webpage.
Note: HTML can be supported by Chrome, Safari, Edge/Internet Explorer, Mozilla, Opera, Brave, etc.
There are different free html editors available where you can write your HTML code. You can write HTML code in your system editor, like Notepad or the third-party editors such as Notepad++, Brackets, Sublime Text, VS Code, or an online code editor like W3School, CodePen pen etc.
Here are some screenshots of different code editors, such as Notepad, Sublime Text, VSCode, and Codepen, and their respective HTML Code.
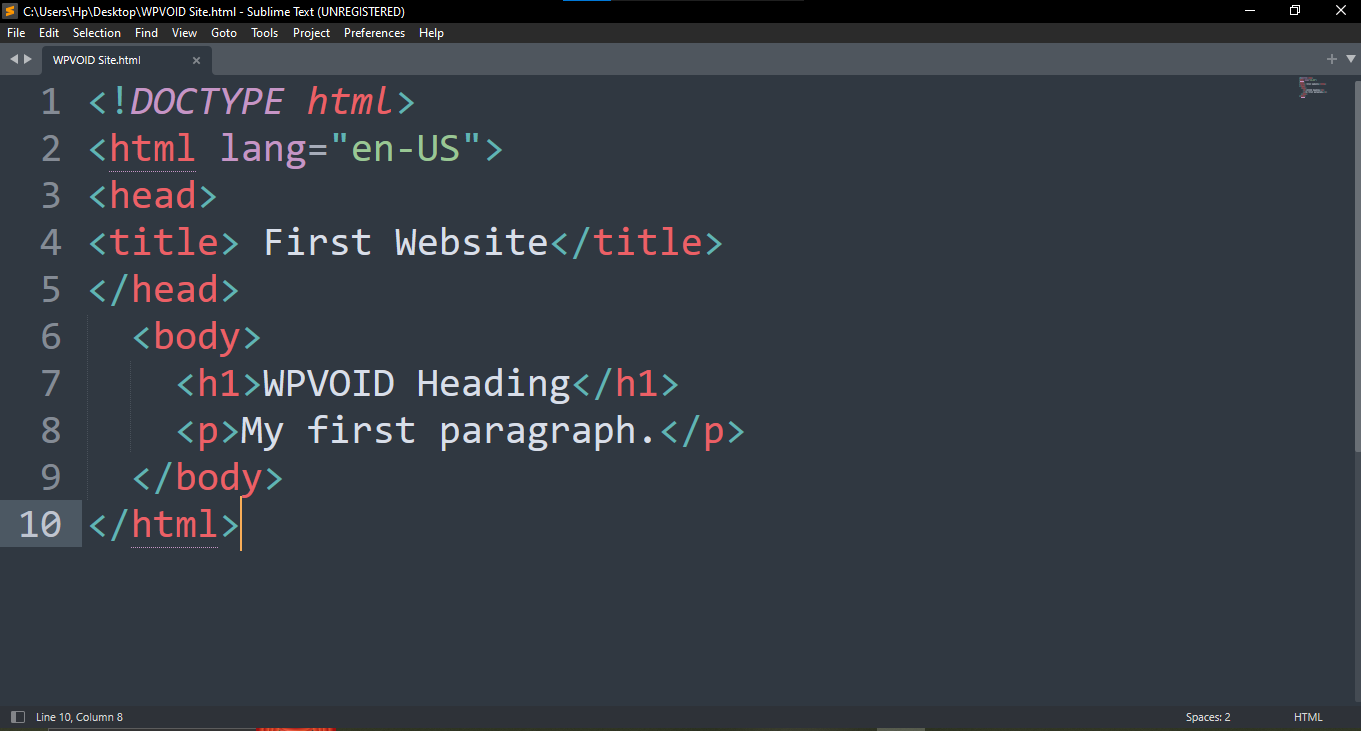
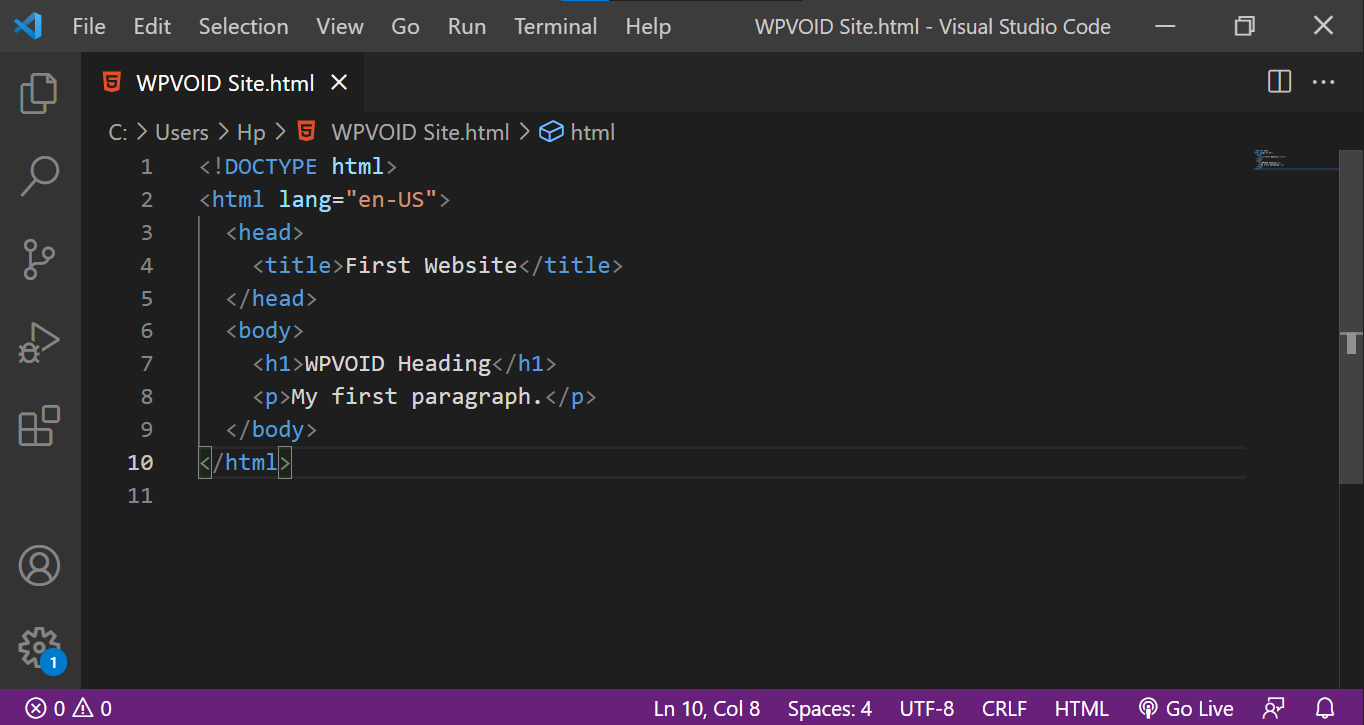
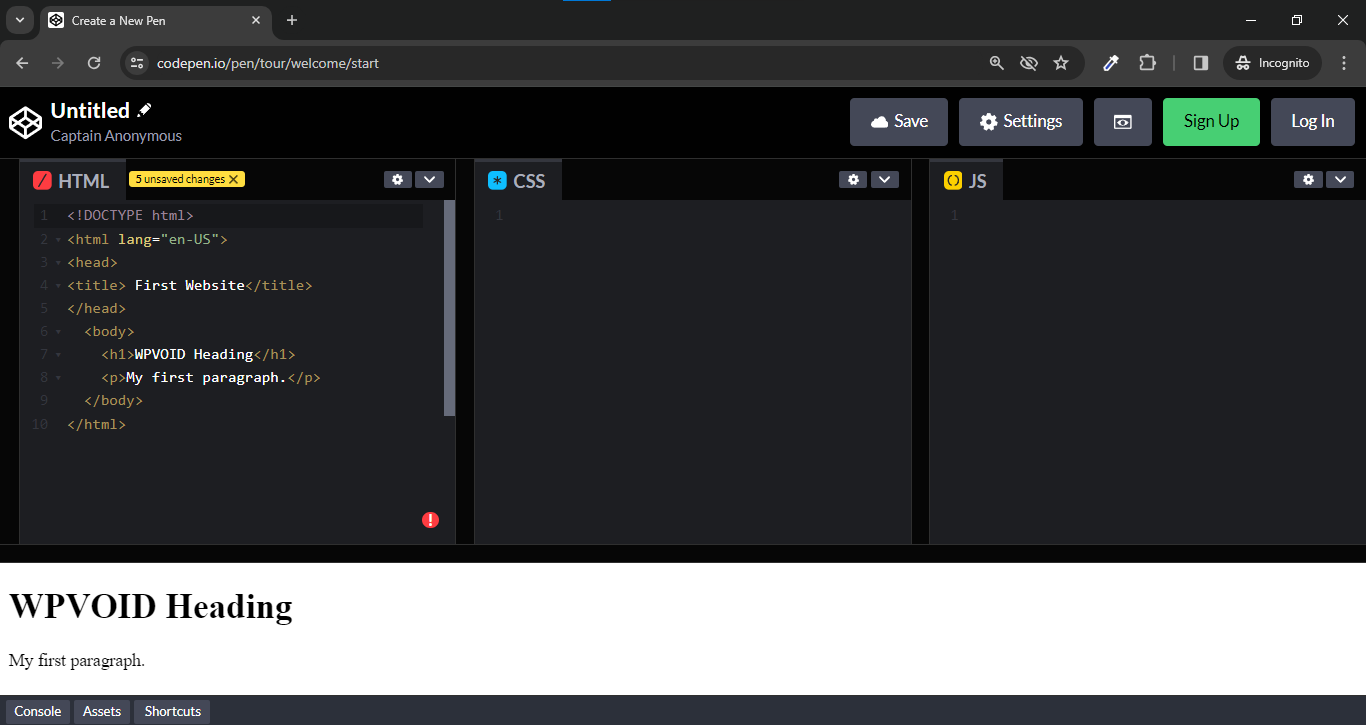
Moreover, these code editors can be used to write other languages like CSS, JS, Python, React, Angular, and many other web creation languages. You can choose the editor based on its file size and your requirements. In the side note, VS Code is more prominent and the most commonly used editor by many web developers, as it supports other languages too.
To become a hireable front-end developer, you need to build an HTML foundation by adding CSS for styling and JavaScript for website interactivity. Moreover, a framework like Bootstrap will help you make your website responsive and device-compatible.
Having an HTML foundation, CSS, JS, framework like Bootstrap, and adding Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress can significantly maximize your value in the global job market and help you to land a job.
HTML is the absolutely essential first step because it builds the structure, or "skeleton," of every webpage globally. To build a functional website, you must learn CSS for design and JavaScript for interaction and functionality in the website. PHP or Node.js can be used as a server-side language to handle the back-end, and MySQL to manage the database.
If you want to expand your portfolio, go with the advanced frameworks like React, Django, or Laravel. Moreover, adding Content Management Tools such as WordPress will be extremely helpful as it widens your opportunities in the web development journey.
It is absolutely worthwhile to learn HTML in 2026, as it remains the single most important language on the web. HTML is the universal, mandatory language used by over 95% of websites. Browsers rely on this essential markup to provide structure, content, and the digital experience's foundation.
Even with the rapid evolution of AI tools, basic HTML knowledge is crucial. If you rely solely on AI, you will lack the necessary foundation to debug, customize, or manually fix the resulting code. The knowledge of HTML is critical that allow you to audit the AI's output and guarantee the final code is efficient.
Furthermore, a deep understanding of HTML is needed for proper integration. This will allow you to understand the meaning of vital HTML elements like ,<head> , <body>, <nav>, and <section>. Also, the knowledge of HTML is beneficial while integrating scripts, especially JavaScript, or embedding third-party tools in your website. To conclude, learning HTML is worth it for decades.
"You must have heard it. If you haven’t, there is a meme about hacking NASA with HTML. Can we really hack NASA with HTML? The answer is no. So, what does this meme actually mean? We will explain it.
We can edit the content of any website using Inspect Element. This tool allows you to change the content of any website, but only on your own computer. It does not change anything on the server side."
Disclaimer: Please do not use this method or trick to mislead the real information. Doing this may get you in trouble.
Step 1: Right-click on the website -> Select Inspect (In Windows)
Command+Option+i (in Mac)
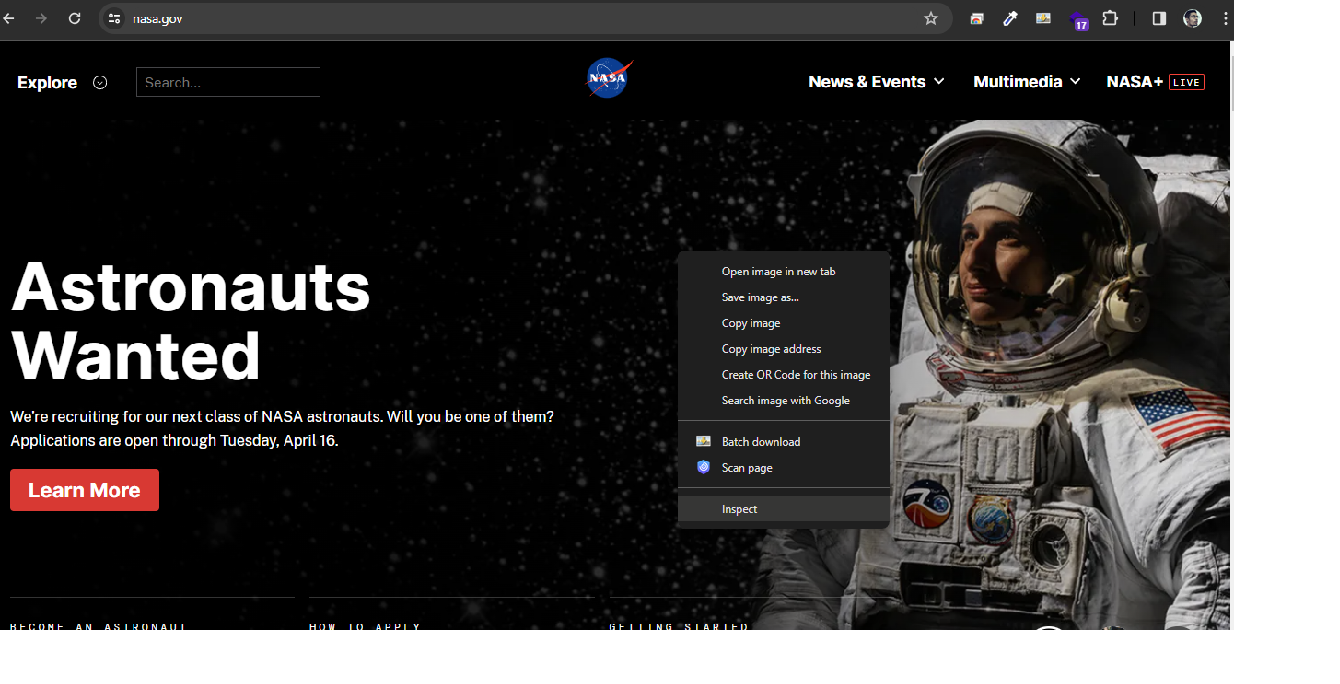
Step 2: Click on an arrow icon.
Step 3: Click on the elements you want to change
Step 4: Double-click on the elements and change the text
Step 5: Change the text/content. Close it by clicking the cross symbol.
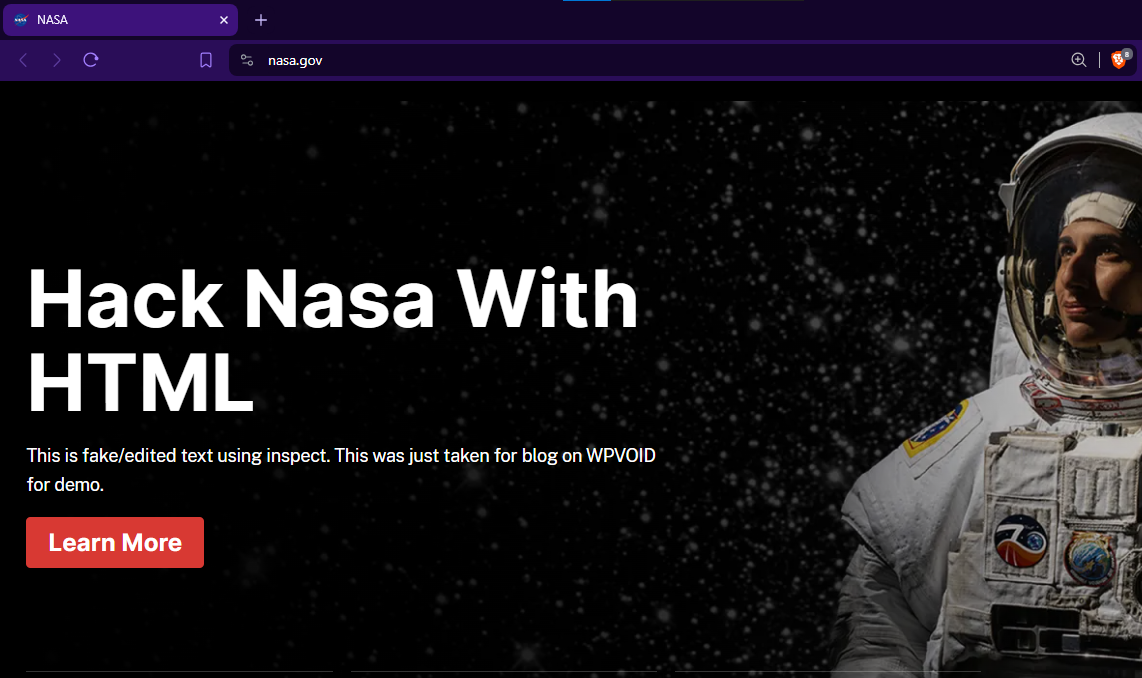
This is how you can change the content of the website using Inspect Element; however, you need to keep in mind that the real information will show once you refresh the page. This trick or method can be very useful in your development process, where you can view the design without changing the server code.
There are many excellent online blogs and articles written for HTML; you can simply search the web. We personally recommend using W3Schools for comprehensive guides, as it is also highly recommended by many developers. You can find full details on tags, elements, forms, and many other features of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
For further study, we also highly suggest checking out MDN Web Docs (Mozilla Developer Network) and freeCodeCamp for in-depth tutorials and projects.
What are iframes?
An iframe () is an HTML tag that is used to embed another independent HTML document or external webpage within the current document. For instance, you can embed a video or map content in your website from a different source using an inline frame without disrupting the parent page's layout. </p>
What is the difference between HTML and HTML5?
HTML is the first version, which lacks the capabilities and supports such as semantic tags (<nav>, <article>), native support for audio and video without plugins, and advanced features like Canvas for graphics, which is present in HTML5. HTML5 is the latest and final version of HTML in 2026.
What is semantic HTML?
Semantic HTML means the HTML tags that can define the meaning or semantics of the content, not just its appearance. To cite an example, tags like <header>, <footer>, and <main> are semantic tags that are used to structure content logically, which improves accessibility and SEO.
What are the 10 basic HTML tags?
The 10 common and basic HTML tags are <html>, <head>, <title>, <body>, <h1> (for headings), <p> (for paragraphs), <a> (for links), <img> (for images), <div> (for division), and <br> (for line break).
What is HTML formatting?
HTML formatting means using the specific tags to define the presentation or style of text within a webpage, such as making text bold (<b> or <strong>), italic (<i> or <em>), or underline (<u>).

